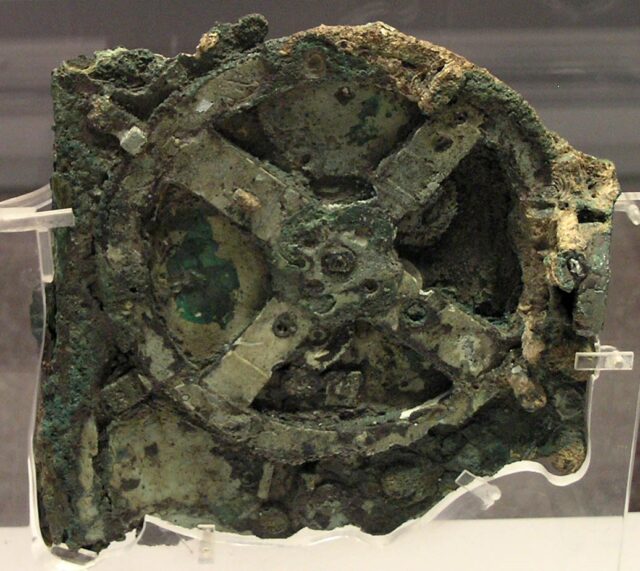
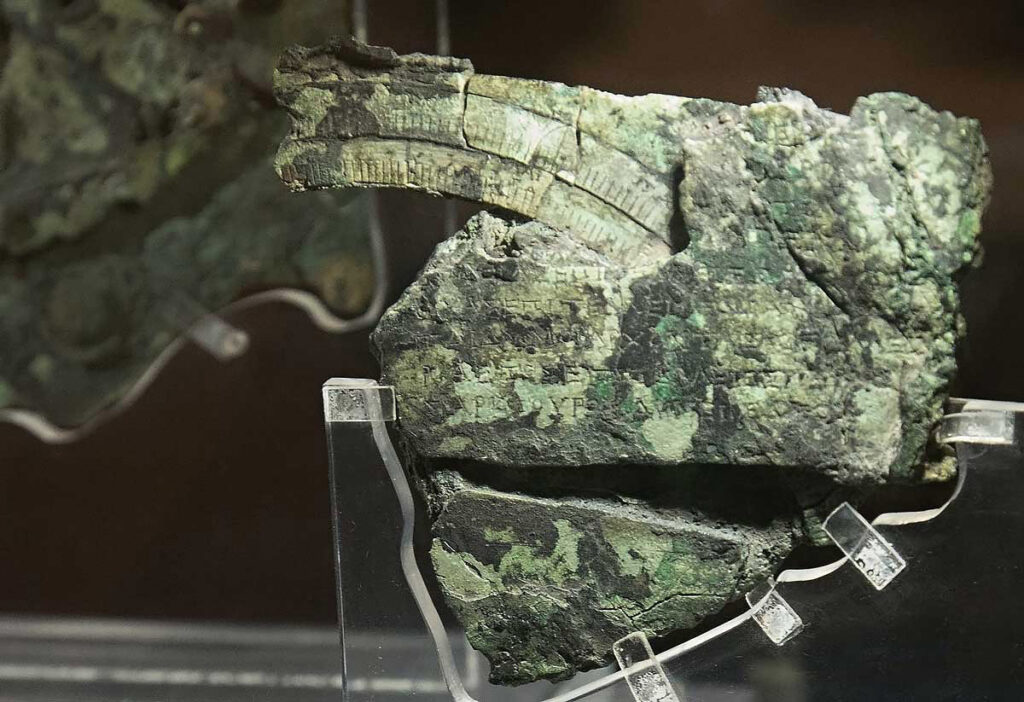
The Antikythera mechanism is an ancient Greek device that was discovered in the early 20th century on the Greek island of Antikythera. It is a complex mechanical device that was used to calculate astronomical positions and predict eclipses, and is considered to be the oldest known example of a geared mechanism in existence.
The device is made up of a series of interlocking gears and dials that were used to represent the positions of the sun, moon, and planets in the sky, as well as the phases of the moon and the dates of solar and lunar eclipses. The Antikythera mechanism is thought to have been built around the 2nd century BC, and is considered to be an important example of ancient Greek technology and scientific knowledge.
The Antikythera mechanism is a particularly ingenious and advanced device for its time. It contained more than 30 gears and featured a series of dials and displays that were used to track the movements of the celestial bodies. The operation of the device was powered by a hand crank, and it could also be used to measure time and determine the positions of the moon and planets on a specific date.
The mechanism is an exceptionally early example of a mechanical computer, and it continues to be a source of fascination for scientists and historical technology enthusiasts. Researchers have studied the mechanism in great detail, and have been able to reconstruct much of its operation through the use of X-ray imaging and computer modeling. Despite its age, the Antikythera mechanism remains a testament to the ingenuity and scientific knowledge of the ancient Greeks, and is considered to be one of the most important archaeological discoveries of the 20th century.
Footnote
- Sources: Aerospace dashboard, funkystuff.org
- Outgoing: NASA
- Keywords: Astronomy, astronomie, mechanisme