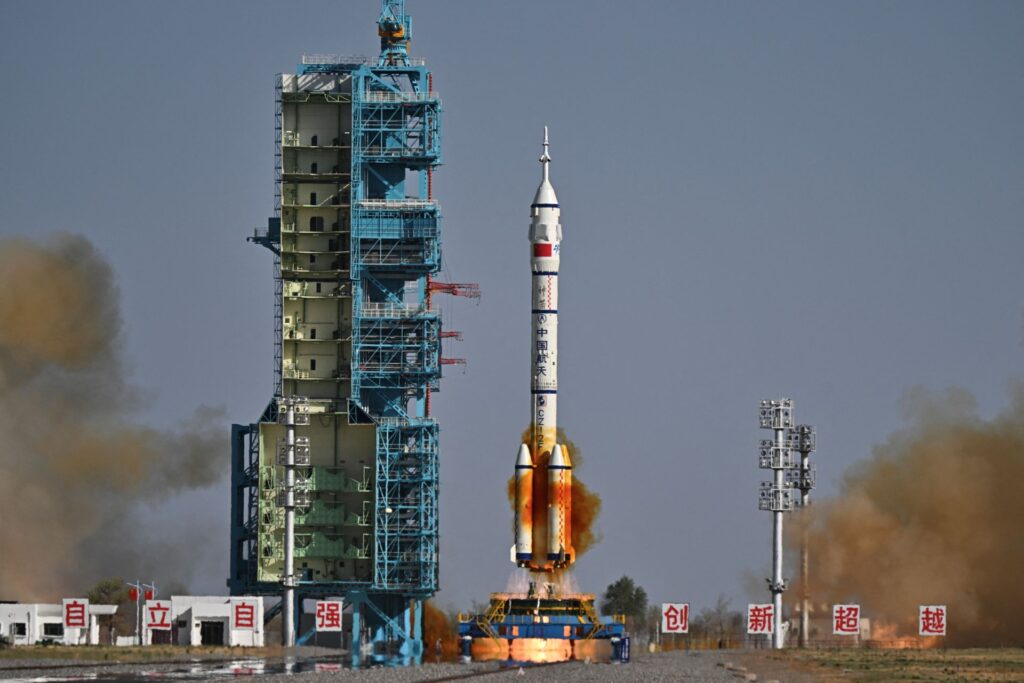
CNSA (China National Space Administration) is the national space agency of China. Headquartered in Haidian, Beijing, it is responsible for China’s civil space programs and international space cooperation.
CNSA
- CASC, China Aerospace Science Corporation
- CCTV, China Central Television
- CMS, China Manned Space Program
- CNSA TV, China National Space Administration
Mars
- Tianhe (on Mars)
- Tianwen 1 (Mars orbiter)
- Zhurong (Mars rover, communication lost)
Moon
- Chang’e 3 Rover front side (2013)
- Chang’e 4 Rover Back side (2019)
- Chang’e 5 Sample return front side (2020)
- Chang’e 6 Sample return back side (2024, southpole, Aitken basin)
- International Lunar Research Station Cooperation Organization (ILRSCO)
- ILRS Moon base
Navigation/Communication
- Qianfan (like Starlink, 14.000 satellites, 800 km)
Rockets
- Deep Blue Aerospace (hopper)
- Falcon Heavy Clone (expected)
- Galactic Energy (hopper)
- Gravity-1 (OrientSpace, private company, 2024, solid fuel, 4 boosters, all solid)
- Gravity-2 (OrientSpace)
- Gravity-3 (OrientSpace)
- Jielong-3 (Smart Dragon, SD 3, solid fuel)
- Kinetica-1 (solid fuel)
- Long March LM 2F
- Long March LM 5 (heavy)
- Long March LM 5B
- Long March LM 5G
- Long March LM 6
- Long March LM 6A
- Long March LM 7A
- Long March LM 7B
- Long March LM 8
- Long March LM 9 (heavy)
- Long March LM 10 (new, ship and lunar lander seperate in space, Moon, 2029)
- Long March LM 11
- Shenzhou (crewed spacecraft)
- Space plane (reusable mini shuttle, made by CASC)
- Tianwen-1 (Mars rocket)
- Tianwen-3 (Mars sample return mission, 2030)
- Tianzhou (cargo ship for TG 1)
- Zhuque-2 rocket (LandSpace, private company, first methane-fueled rocket in orbit, LOX, 2023)
- Zhuque-3 (OrientSpace, Methane and Lox). 03-12-2025 Zhuque-3 rocket achieved orbit in its first launch but the booster failed to make a landing.
China Spaceports
- Launch (Sorted by latitude):
- Jiuquan (JSLC) Satellite Launch Centre (Gobi desert, northwest China). Jiuquan Gansu Province Human spaceflight, manned missions to orbit. Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center (JSLC).
Location: Gobi-woestijn, Inner Mongolia.
Coordinates: 40.96056° N, 100.29833° E. - Taiyuan (TSLC) Shanxi Province Polar and medium/low orbit satellites. Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center (TSLC).
Location: Kelan County, Shanxi Province.
Coordinates: 38°50′56.71″ N, 111°36′30.59″ E. - Xichang (XSLC) Sichuan Province Geostationary satellites, lunar probes, and powerful rockets. Xichang Satellite Launch Center (XSLC).
Location: Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province.
Coordinates: 28.24646° N, 102.02814° E. - Wenchang (Hainan) Island Heavy-lift rockets, such as the Long March 5 and 7. Wenchang Space Launch Site (WSLS)
Location: Hainan Island (peninsula).
Coordinates: 19°36′52.17″ N, 110°57′4.08″ E.
- Jiuquan (JSLC) Satellite Launch Centre (Gobi desert, northwest China). Jiuquan Gansu Province Human spaceflight, manned missions to orbit. Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center (JSLC).
- Landing:
Siziwang Banner (Inner Mongolia) 42°16′43″ N, 111°36′49″ E. Commonly used landing zone for capsules such as Chang’e 5.
Dongfeng Landing Site (Inner Mongolia) 41°23′20″ N, 99°58′53″ E.
Space stations
- Tiangong (TG-1, space station CSS)
- Tiangong (TG-2, space station CSS)
- Tianhe (basic module CSS)
- Wengian (research module CSS)
- Mentian (research module CSS)
CNSA progress
- 05-11-2025 Investigations revealed that small cracks had developed in a window of the Shenzhou-20 capsule. These are likely the result of space debris. Damaging the heat-shielding exterior or parachute of the Shenzhou-20 re-entry capsule. One week delay of the return flight.
- 13-11-2025 Return flight with Shenzou-21.
- 24-11-2025 Launch of Shenzhou-22 (with a Long March 2F) capsule for the 3 taikonauts stuck on Tiangong space station (LEO). Launch from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. Docking at forward port 3.5 hours later.
- 03-12-2025 Zhuque-3 rocket achieved orbit in its first launch but the booster failed to make a landing.
Keywords
- Taikonaut
- Space weather