ESA Ariane 6 progress and sequence of events
For the development of Ariane 6, ESA is working with an industrial network of several hundred companies in 13 European countries, led by prime contractor ArianeGroup.
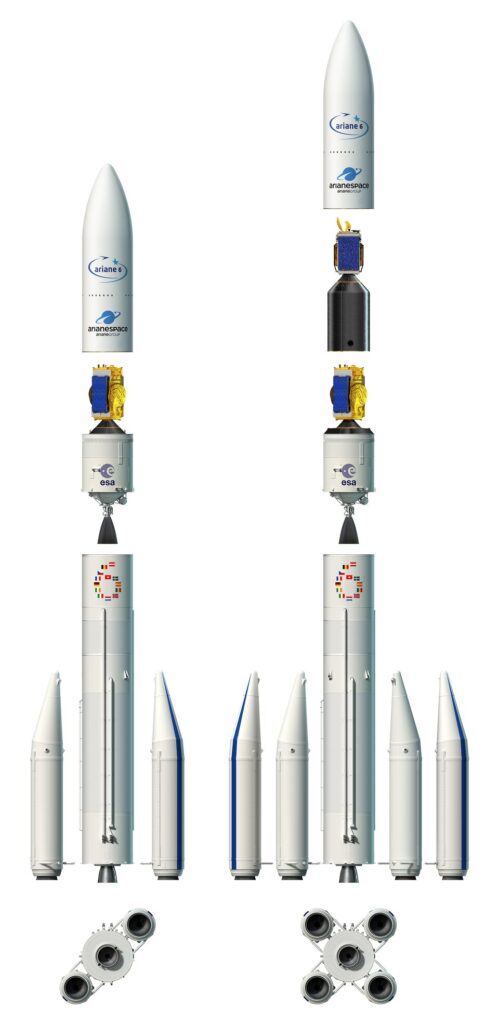
Ariane 6 is a European expendable launch system developed by ArianeGroup on behalf of the European Space Agency (ESA). It replaces the Ariane 5, as part of the Ariane launch vehicle family. The stated motivation for Ariane 6 (as of 2015) was to halve the cost compared to Ariane 5, and increase the capacity for the number of launches per year (from six or seven to up to eleven).
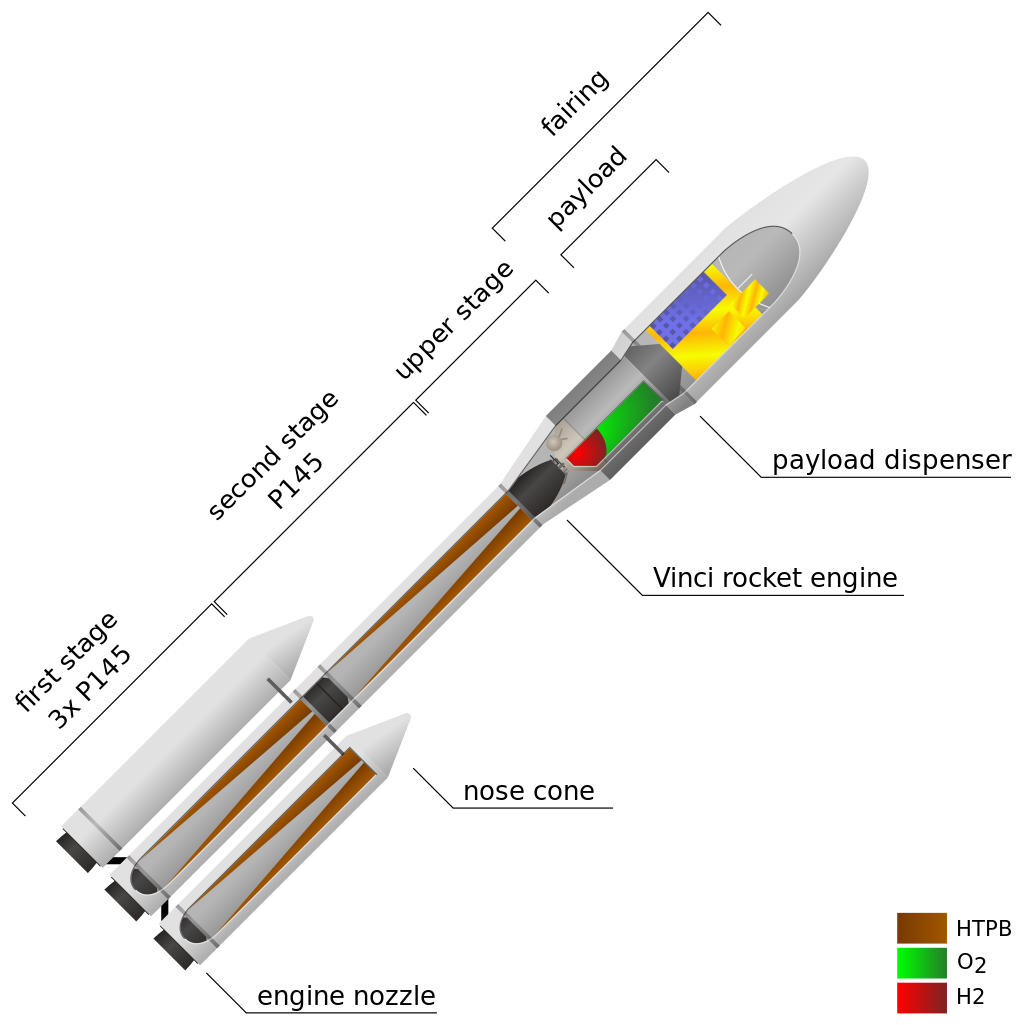
Ariane 6 Elements
Ariane 6 comprises three stages: two or four strap-on boosters, and a lower and upper stage – the central core.
The lower stage with solid rocket boosters propels Ariane 6 in the first phase of flight, delivering 135 tonnes of thrust in vacuum. The core stage is powered by the liquid-fuelled Vulcain 2.1 – an upgraded engine derived from Ariane 5’s Vulcain 2 – and either two or four P120C boosters to provide additional thrust at liftoff.
The upper stage is powered by the reignitable Vinci engine fuelled by cryogenic liquid oxygen and hydrogen. This allows Ariane 6 to reach a range of orbits on a single mission to deliver more payloads. The upper stage will typically burn one, two or more times to reach the required orbits. After separation of the payload, there will be a final burn to deorbit the upper stage, to mitigate space debris.
The ogive-shaped fairing at the top of Ariane 6 is available in two sizes: 20 m (A64/A62) and 14 m (A62). Both are 5.4 m in diameter and made of carbon fibre-polymer composite. The fairing protects satellites from the thermal, acoustic and aerodynamic stresses on the ascent to space.
Ariane 6 Launch zone
Ariane 6 will be launched from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana from a dedicated launch site 4 km west of the Ariane 5 launch pad. The main structures include the Launch Vehicle Assembly Building, the mobile gantry and launch pad.
The Spaceport covers 170 hectares, with buildings on 18 hectares. Its location is ideal; with open sea to the north and east, and the town of Kourou 17 km distant, flight safety constraints are minimised. And, because the Spaceport is just 5° north of the equator, flights to the east gain very nearly the maximum possible speed boost from the Earth’s rotation, increasing payload performance for any rocket – much more than from more northerly or southerly locations.
Ariane 6 Lower Liquid Propulsion Module
The first stage of Ariane 6 is called the Lower Liquid Propulsion Module (LLPM). It is powered by a single Vulcain 2.1 engine, burning liquid hydrogen (LH2) with liquid oxygen (LOX). Vulcain 2.1 is an updated version of the Vulcain 2 engine from Ariane 5 with lower manufacturing costs.[clarification needed] The LLPM is 5.4 m (18 ft) in diameter and contains approximately 140 tonnes (310,000 lb) of propellant.
Ariane 6 Solid Rockets (ESR)
Additional thrust for the first stage will be provided by either two or four P120 Solid rocket boosters, known within Ariane 6 nomenclature as Equipped Solid Rockets (ESR). Each booster contains approximately 142 tonnes (313,000 lb) of propellant and delivers up to 4,650 kN (1,050,000 lbf) of thrust. The P120 motor is also first stage of the upgraded Vega C smallsat launcher. The increased production volumes through sharing motors lowers production costs.
The first full-scale test of the ESR occurred at Kourou on 16 July 2018, and the test completed successfully with the thrust reaching 4,615 kN (1,037,000 lbf) in vacuum.
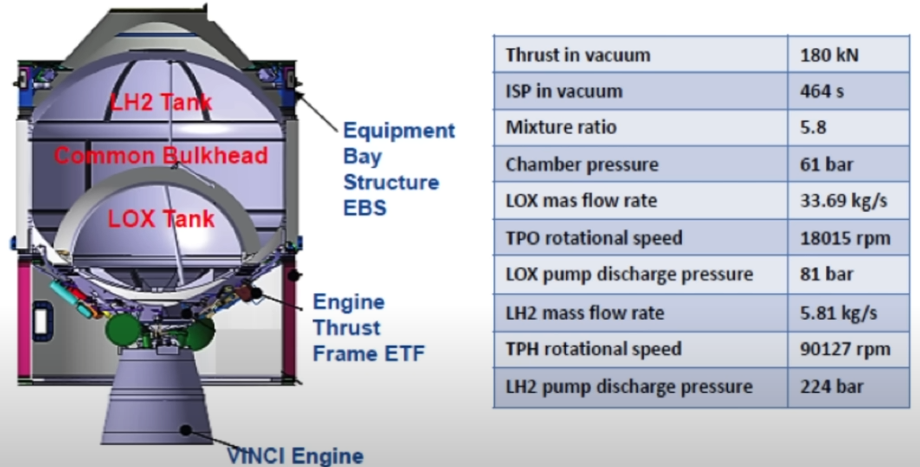
Ariane 6 Upper Liquid Propulsion Module
The upper stage of Ariane 6 is called the Upper Liquid Propulsion Module (ULPM). It features the same 5.4 m (18 ft) diameter as the LLPM, and also burns liquid hydrogen with oxygen. It is powered by the Vinci engine delivering 180 kN (40,000 lbf) of thrust and enabling multiple restarts. The ULPM will carry about 31 tonnes (68,000 lb) of propellant.
Ariane 6 Orbital types
- LEO = Low Earth Orbit.
- SSO = Sun-Synchronous Orbit (heliosynchronous).
- GTO = Geostationary Transfer Orbit .
- MEO = Medium Earth Orbit (Earth-centered orbit with an altitude).
- Sun-Earth L2 orbit = For space-based observatories, Lagrange point.
- Areocentric orbit= Around the planet Mars.
- TLI = Trans-Lunar Injection orbit.
- Halo = Periodic, three-dimensional orbit associated with one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics.
- Heliocentric orbit = Superseded astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe.
Ariane 6 Configurations
- Ariane 5 ES
- Mass 775 t
- Payload capacity 21 t (300 km LEO)
- First flight 09-03-2008
- 3 solid boosters
- Ariane 62
- Mass 530 t
- Payload capacity 4,720 kg (GTO)
- Ariane 64
- Mass 860 t
- Payload capacity 5,000 kg (GTO)
Ariane 6 Dutch contribution
- Airbus Netherlands (in Oegstgeest): Ariane 6, Parts to which the rocket engines are attached. Vinci engine mounting.
- Airbus Netherlands: Ariane 6, Motorframe (cross and stabilizer).
- Airbus Netherlands: Ariane 6, Aluminum cylinders (seventh to ninth launch).
- Aerospace Propulsion Products (APP in Klundert): Ariane 6, Inflammatory Mechanisms. Main engine suspension panels (thermal protection). Ignition mechanism.
Ariane 6 Completed 2014-2023
- 00-12-2014 Design concept Ariane 6 by ESA. Replacing Ariane 5.
- 00-00-2015 High-level design phase.
- 00-00-2016 Design phase.
- 16-07-2018 First full-scale ESR test completed successfully with the thrust reaching 4,615 kN (1,037,000 lbf) in vacuum.
- 00-05-2019 Arianespace placed the first production order.
- 18-07-2023 Combined test: First fueling and init countdown leading to engine ignition.
- 05-09-2023 First ignition of the Vulcain 2.1 engine on the launch pad.
- 23-10-2023 A 30-hour-long chronology including additional qualification tests.
- 23-11-2023 Full-scale firing Vulcain 2.1 engine covering the core stage flight phase.
- 15-12-2023 Launch countdown robustness qualification in degraded conditions, including abort launch and emergency draining propellant.
Ariane 6 Completed 2024
- 30-01-2024 Disconnection of cryogenic connection systems and umbilicals both electrical and ventilation systems.
- 05-02-2024 Disconnection of cryogenic connection systems and umbilicals both electrical and ventilation systems.
- 21-02-2024 Arrival of the flight stages from Europe on board the Canopée in Pariacabo Harbour, Kourou.
- 28-02-2024 The main stage and the upper stage of the inaugural flight of Ariane 6 have been unloaded at the launcher assembly building (BAL) and their integration has begun.
- 11-03-2024 The first booster from the inaugural flight of Ariane 6, integrated into the booster finishing building, was moved to the launcher integration building for storage.
- 13-03-2024 The Ariane 6 model which remained on the launch pad for more than a year and used for the qualification of the new launcher has been completely dismantled and the launch pad is now free for preparations for the inaugural flight of Ariane 6 .
- 14-03-2024 The second booster for the inaugural flight of Ariane 6 has begun to be integrated into the booster finishing building in French Guiana.
- 14-03-2024 Press release by the ESA, preparing for launch (between 15-06-2024 and 31-07-2024)
- 15-03-2024 The upper floor and the main floor are now connected to form the central body. The Upper Liquid Propulsion Module and the Lower Liquid Propulsion Module were assembled horizontally at the Launcher Assembly Building (BAL) to form the central body of Ariane 6.
- 18-03-2024 Integration of the core stage in launcher integration building.
- 00-04-2024 Second booster ready.
- 00-04-2024 Verticalization of the central body.
- 00-05-2024 Payloads arrival in Kourou.
- 14-06-2024 All stages of the first Ariane 6 rocket have been transferred to the launch pad in French Guiana – marking the beginning of operations.
- 20-06-2024 Operators first let the 295-foot (90-meter) rocket stand free on the pad, without support from its gantry, for the first time ever. Then, they cooled the rocket to cryogenic temperatures and pumped it flush with fuel, conducting systems checks all the while, before completely draining it in preparation for the actual launch. ESA will release detailed results from the test later this week, but so far, Ariane 6 appears to be functioning as planned, mission managers said.
- 04-07-2024 Ariane 6 is cheaper than Ariane 5, and slightly more expensive than SpaceX’s Falcon 9. The price per launch of Ariane 6 varies depending on the choices the customer makes.
- 08-07-2024 Places have already been booked by commercial clients at approximately 30 launches.
- 09-07-2024 The first time that all parts of Ariane 6 are simultaneously exposed to the full load. The first stage engine is as powerful as a hundred Joint Strike Fighters and quickly accelerates Ariane 6 to twice the speed of a bullet leaving a gun.
- 09-07-2024 Inaugural Launch. Three-hour window 20:00 to 23:00 CEST. Postponed 1 hour because of issue in the data acquisition system. Actual launch at 21:00 CEST. Daylight in Kourou.
- 09-07-2024 Anomaly APU under investigation.
Flight 1 Characteristics (09-07-2024)
- Ariane 6 Flight 1 (Inaugural flight).
- Launch date: 09-07-2024.
- Launch location: Kourou, French Guiana.
- Rocket type: Ariane 62.
- Orbit: LEO.
- Mission: Demonstration
- Payload: Multiple rideshare.
- Customers: PTS, TU Berlin, ArianeGroup, BarcelonaTech, NASA, TUKE, University of Lisbon.
- Three-hour window 20:00 to 23:00 CEST. Postponed 1 hour because of issue in the data acquisition system. Actual launch at 21:00 CEST. Daylight in Kourou.
- The inaugural launch’s flight plan Ariane 6 up to low Earth orbit (LEO) at an altitude of 320 miles (520 kilometers). This launch will not just be a test flight – once up in orbit, the rocket will release nine cubesats. Also aboard Ariane 6’s Vinci upper stage are four non-orbital experiments, including a device that will test a system for rapidly locating satellites and two capsules that will drop from orbit into the Pacific in order to test if they can re-enter Earth’s atmosphere successfully.
- Vinci will burn up. The upper stage can be refired multiple times once in orbit, which can allow a single launch to deploy multiple satellites at different altitudes – and, as is planned for this first flight – deorbit the spacecraft and prevent it from floating endlessly as debris or falling to Earth uncontrolled.
- The stakes for Europe’s launch capabilities are high. Ariane 6 is intended to replace the venerable Ariane 5, which took off for the final time last year after 117 launches and 27 years of service. Since then, European launches have been dependent on other – largely American – vehicles.
- In these last days before launch, ESA and its partners are keen to emphasize their dissatisfaction with this post-Ariane 5 status quo – and the opportunity for Ariane 6 to change it if successful. “It is an important moment in European space history and for the sovereignty of Europe,” said Carina Laveau, director of space transportation at CNES, France’s national space agency.
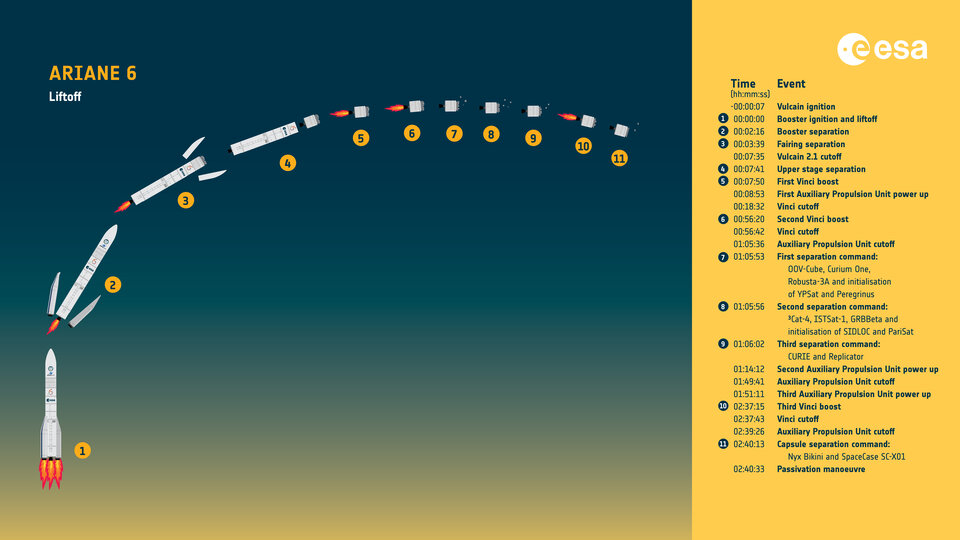
Flight 1 Sequence of events (09-07-2024)
Ariane 6 is assembled horizontally, the transferred to the pad where it is raised vertically thanks to the gantry. The fairing with the satellites inside is hoisted and connected to the top. The mobile gantry protects the launcher during preparations on the pad and it allows the teams to work on the rocket until shortly before liftoff. There are 22 levels with platforms. Cryo technic propellant runs through 300 meter pipes under the ground. Shortly before launch the mobile gantry will be removed.
MET hh:mm:ss
- T-05:30:00 Weather check (20 km radius, no wind during fueling up, lightning risk, weather balloons)
- T-05:30:00 Start countdown clock (hh:mm:ss)
- T-05:00:00 Rollback gantry
- T-05:00:00 Removal of the mobile gantry.
- T-05:00:00 Launch pad clear.
- T-05:00:00 Electrical test.
- T-05:00:00 Fluid System Test.
- T-05:00:00 Weather check
- T-01:00:00 Propellant loading core stage (LOX).
- T-01:00:00 Propellant loading core stage (LH2).
- T-01:00:00 Propellant loading upper stage (LOX).
- T-01:00:00 Propellant loading upper stage (LH2).
- T-00:06:00 Weather check
- T-00:05:00 Five-minute callout by Launch Director (LD)
- T-00:05:00 Clock reset and sync
- T-00:04:00 Ariane 6 autonomous
- T-00:01:30 Tanks topped off
- T-00:01:00 One-minute callout by LD
- T-00:00:07 Vulcain engine ignition
- T-00:00:07 When Vulcain engine is running smooth the boosters are ignited
- T-00:00:07 Retract fueling arms
- T-00:00:00 Booster ignition
- T-00:00:02 Ariane 6 liftoff
- T+00:02:16 Booster cutoff
- T+00:02:16 Booster separation
- T+00:03:39 Fairing separation (alt 118 km, dist 240 km, speed 2,06 km/s)
- T+00:07:35 Vulcain engine cutoff (MECO)
- T+00:07:41 Vulcain engine separation
- T+00:07:50 Vinci engine ignition (first)
- T+00:08:53 APU power up (first) Auxiliary Propulsion Unit (APU) is a small system that plays a vital role by pressurising the fuel tanks during flight and providing additional thrust on demand. It is the key to the reignition of the Vinci engine. APU is using fuel from the two main tanks. It has two thrusters on the rear side of upper stage. For a reignition are needed: 1. Tank pressures, 2 Tank temperatures (cooling in sunshine), 3 Quality (position) of the fuel. Fuel is floating in space, we need the fuel close to the tank bottom, APU creates some artificial gravity.
- T+00:18:32 Vinci engine cutoff (first)
- T+00:54:00 Coasing phase (first). APU is still running.
- T+00:55:00 Telemetry: alt 550 km, distance 18.679 km, speed 7,33 km/s.
- T+00:56:20 Vinci engine ignition (second)
- T+00:56:42 Vinci engine cutoff (second)
- T+01:05:36 APU cutoff (first)
- T+01:05:53 Separation command (first) (OOV-Cube, Curium One, Robusta-3A and initialisation of YPSat and Peregrinius) (8)
- T+01:05:56 Separation command (second) (3Cat-4, ISTSat-1, GRBBeta and initialisation of SIDLOC and PariSat, LIFI, Exopod Nova, RAMI).
- T+01:06:02 Separation command (third) (CURIE and Replicator).
- T+01:14:12 APU power up (second)
- T+01:49:41 APU cutoff (second)
- T+01:51:11 APU power up (third)
- T+01:51:11 Coasting phase (second) Demonstration phase: Operation in micro gravity.
- T+01:58:00 Anomaly occurred. APU confirmation of power up (T+01:51:11). But APU switches itself off again due to safety measures on board. No re-ignation is allowed when the spacecraft is not safe. Consequence: Stable altitude but deviation from planned trajectory. De-orbit burn not been succesfully completed. Not or different performed:
- T+02:37:15 Vinci engine ignition (third) Without the APU, the rocket was not able to restart its Vinci engine for a second time to complete a deorbit burn.
- T+02:37:43 Vinci engine cutoff (third)
- T+02:39:26 APU cutoff (third)
- T+02:40:13 Capsule separation command (Nyx Bikini and SpaceCase SCX01). Not deployed successfully.
- T+00:00:00 Passivation manoeuvre was triggered successfully. Passivation refers to the process of removing stored energy from a vehicle to reduce the risk of high-energy releases (explosions or fragmentations, for example) that could produce unwanted orbital debris.
- T+03:01:14 Upper stage Reentry (and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean).
Ariane 6 Continuation after de inaugural flight (10-07-2024)
- 10-07-2024 According to ESA, data from different ground stations detailing how the upper stage performed will first need to be collated before an analysis of the data can begin. This process is expected to take a few days, and the subsequent analysis to determine what happened to the APU will take between one and two weeks.
- 10-07-2024 Despite not yet understanding what happened to the APU during the inaugural flight, Arianespace CEO Stephane Israel confirmed that the investigation would have no impact on the rocket’s first operational launch, which is expected before the end of 2024.
- 00-00-2024 Flight 2. Rocket type: Ariane 62, Payload: CSO-3, Orbit: SSO, Customer: CNES/DGA.
- 00-02-2025 Flight 3. Rocket type: Ariane 64, Payload: MTG-S1, Orbit: GTO, Customer: EUMETSAT.
Footnotes
- European Space Agency (ESA)
- Rocket engine performance (specific impulse) table
- Guiana Space Centre (Official)
- Guiana Space Centre (Wikipedia)
- Search: Europa, Nederland, VI