Aerospace history
Spaceflight milestones (1880-1961)
- 00-00-1880 Articles by Tsjolkowsky (1857-1935).
- 00-00-1923 Articles by Oberth (1894-1989).
- 16-03-1926 First liquid-fueled rocket by Goddard (1882-1945). Reached 13 meters.
- 00-00-1932 Gyroscopic rocket by Goddard (1882-1945).
- 00-00-1937 V1 and V2 by Wernher von Braun (1912-1977).
- 16-04-1946 First American V2 by Wernher von Braun (1912-1977).
- 00-00-1951 Total of 66 American V2’s launched.
- 00-08-1953 Upgraded V2 called Redstone.
- 00-00-1954 Atlas rocket.
- 04-10-1957 First satellite (Sputnik).
- 12-04-1961 First human in space (Yuri Gagarin).
NASA Rockets (1961-1972)
- Mercury Redstone (1952-1954)
- Thor Delta (Thor from airforce, Jupiter from army with Wernher von Braun)
- Mercury Atlas (1954)
- Atlas Agena
- Atlas Centaur
- Gemini Titan II
- Saturn I
- Apollo Saturn 1B
- Apollo Saturn V
Artemis related spaceflight (1965-2011)
- 00-00-1965 Start of the Deep Space Network (DSN) (used for Rover, New Horizons, Voyager etc.).
- 08-02-1974 Last Skylab flight (SL-4, SLM-3).
- 17-07-1975 Last Apollo-Soyuz flight (one mission only).
- 03-05-1998 Last Spacelab flight (Neurolab, STS-90).
- 20-11-1998 First module International Space Station (ISS) (Zarya, launched by a Proton rocket).
- 02-11-2000 ISS is permanently occupied (ongoing).
- 08-07-2011 Last Space Shuttle mission (STS-135).
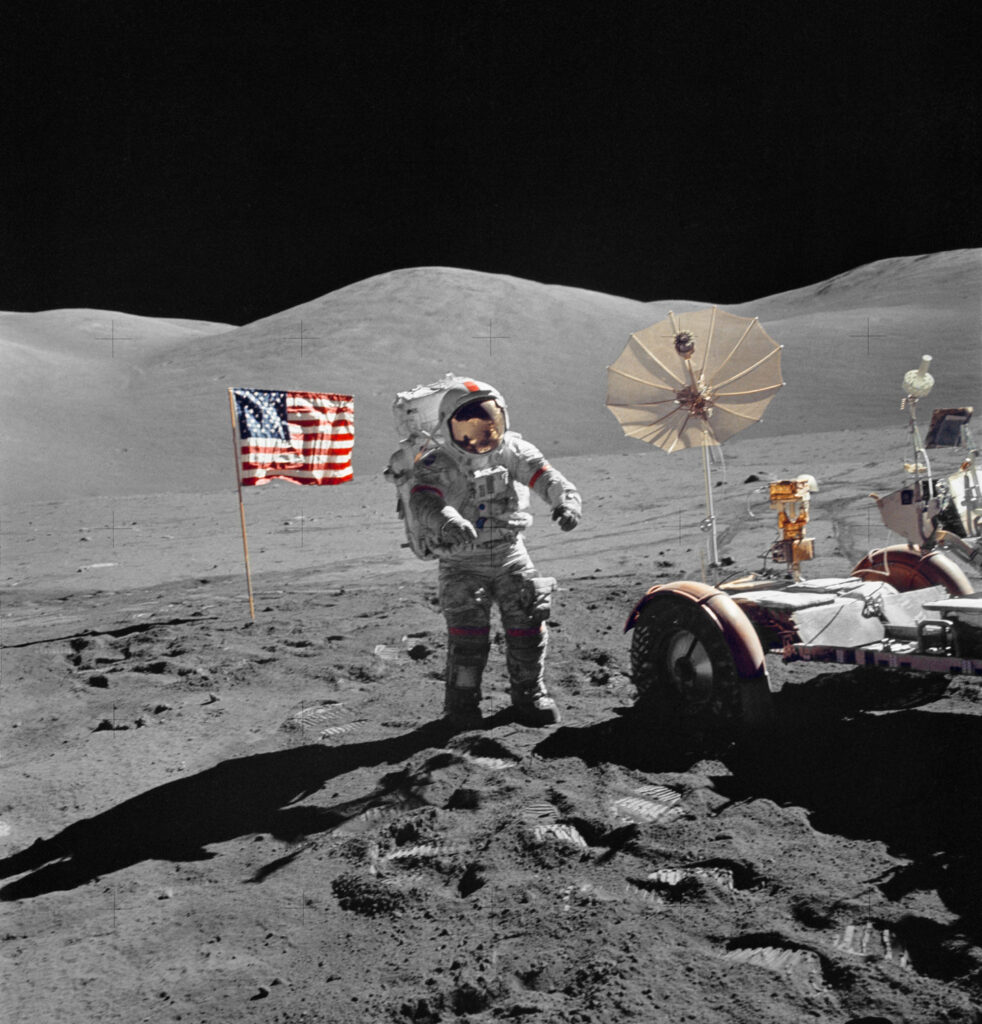
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be remotely operated from ground stations on Earth, or autonomously, without any direct human involvement. People trained for spaceflight are called astronauts or taikonauts (Chinese); and non-professionals are referred to as spaceflight participants or spacefarers.
The first human in space was Yuri Gagarin, who launched as part of the Vostok program on 12 April 1961 at the beginning of the Space Race. On 5 May 1961, Alan Shepard became the first American in space, as part of Project Mercury. Humans traveled to the Moon nine times between 1968 and 1972 as part of the United States’ Apollo program, and have had a continuous presence in space for 21 years and 364 days on the International Space Station (ISS). On 15 October 2003, the first Chinese taikonaut, Yang Liwei, went to space as part of Shenzhou 5, the first Chinese human spaceflight. As of 2021, humans have not traveled beyond low Earth orbit since the Apollo 17 lunar mission in December 1972.
Footnote
- Sources: Aerospace dashboard, NASA astronauts, funkystuff.org,
- Outgoing: NASA
- Keywords: