Rockets and their propellants, overview. Propellant is the chemical mixture burned to produce thrust in rockets and consists of a fuel and an oxidizer. A fuel is a substance that burns when combined with oxygen producing gas for propulsion. An oxidizer is an agent that releases oxygen for combination with a fuel. The ratio of oxidizer to fuel is called the mixture ratio. Propellants are classified according to their state – liquid, solid, or hybrid.
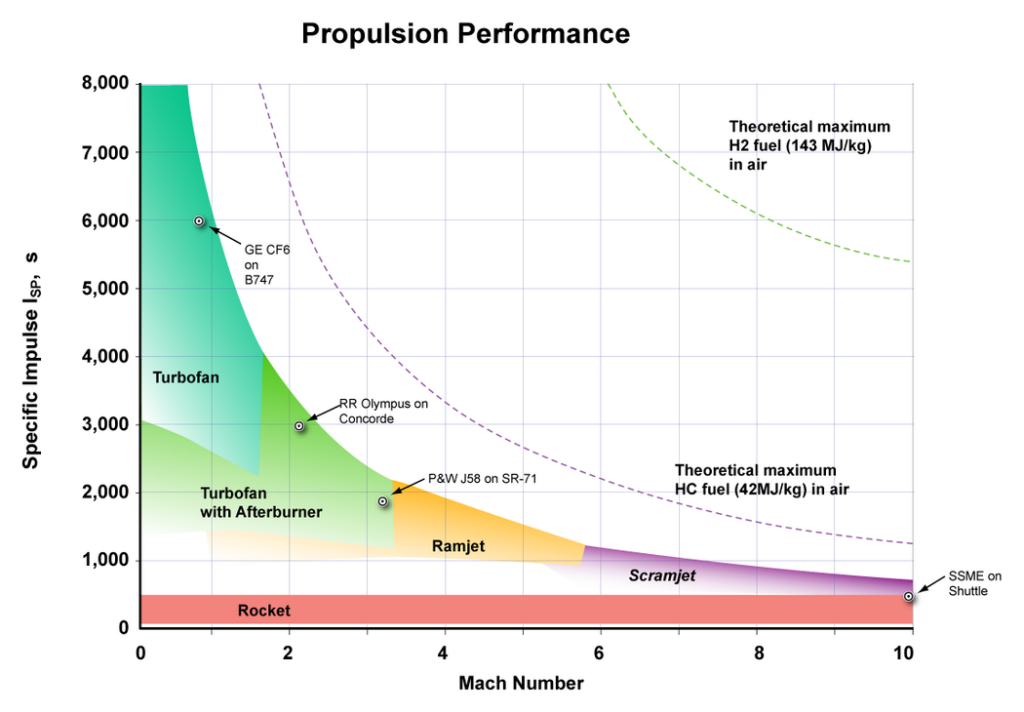
The gauge for rating the efficiency of rocket propellants is specific impulse, stated in seconds. Specific impulse indicates how many pounds (or kilograms) of thrust are obtained by the consumption of one pound (or kilogram) of propellant in one second. Specific impulse is characteristic of the type of propellant, however, its exact value will vary to some extent with the operating conditions and design of the rocket engine.
Specific impulse (ISP)
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated Isp) is a measure of how efficiently a reaction mass engine (a rocket using propellant or a jet engine using fuel) creates thrust. For engines whose reaction mass is only the fuel they carry, specific impulse is exactly proportional to the effective exhaust gas velocity.
Thus, the specific impulse can be defined as the proportion of the speed of expelling the propellant from the nozzle and measured in second. A higher specific impulse is the higher speed of ejection of the propellant. This speed is monitored to measure the quality of the engine, in other terms, how fast the engines burn fuel to lift off the Rocket.
Specific impulse (table)
| Rockets performance (specific impulse) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rocket | Stage | Engines | Propellant | ISP, Specific impulse (in seconds) (vacuum or sea level) |
| Atlas/Centaur (1962) | 1 2 3 |
2 x Rocketdyne YLR89-NA7 Rocketdyne YLR105-NA7 2 x P&W RL-10A-3-3 |
RP-1 / LOX RP-1 / LOX LH2 / LOX |
292 vac 309 vac 444 vac |
| Titan II (1964) | 1 2 |
2 x Rocketdyne LR-87-AJ-5 Rocketdyne LR-91-AJ-5 |
Aerozine 50 / NTO Aerozine 50 / NTO |
259 sl 312 vac |
| Saturn V (1967) | 1 2 3 |
5 x Rocketdyne F-1 5 x Rocketdyne J-2 Rocketdyne J-2 |
RP-1 / LOX LH2 / LOX LH2 / LOX |
260 sl 424 vac 424 vac |
| Space Shuttle (1981) |
0 OMS |
2 x Thiokol SRB (Booster) 2 x Aerojet OMS |
PBAN Solid MMH / LOX |
269 vac 455 vac 313 vac 260-280 vac |
| Delta II (1989) | 0 1 2 |
9 x Castor 4A (Booster) Rocketdyne RS-27 Rocketdyne AJ10-118K |
HTPB Solid RP-1 / LOX Aerozine 50 / NTO |
266 vac 295 vac 321 vac |
| Ariane 5 (2023) |
0 1 |
2 x Booster, P241, EAP (Booster) Vulcain 2, EPC Aestus, EPS L-10 |
HTPB Solid LH2 / LOX MMH / N2O4 |
275 sl 434 vac |
| Ariane 6 (2024) | 0 1 2 |
2 or 4 x Avio P120 (Ariane 62, 64) (Booster) Vulcain 2.1 Vinci |
HTPB Solid LH2 / LOX LH2 / LOX |
278 vac – – |
| VEGA (2012) | 1 2 3 4 |
Avio P80 Zefiro23 Zefiro9 AVUM ModuleRD-843 |
HTPB Solid HTPB Solid HTBB Solid UDMH / N2O2 |
280 vac 288 vac 296 vac 315 vac |
| VEGA-C (2022) | 1 2 3 4 |
2 or 4 x Avio P120C Zefiro40 Zefiro9 AVUM+ |
HTPB Solid HTPB Solid HTPB Solid UDMH / N2O2 |
278 vac 293 vac 294 vac 315 vac |
| Terran 1 (2023) | 1 2 |
9 x Aeon 1 Aeon 1 Vac |
CH4 / LOX CH4 / LOX |
360 vac 360 vac |
| Starship (2023) | 1 2 |
Raptor 2 (Raptor 3 = +18%) Raptor vac |
CH4 / LOX CH4 / LOX |
350 vac 380 vac |
| SLS (5 block) (2022) | 0 1 2 |
2 x Orbital ATK 5 segment (Booster) 4 x Rocketdyne RS-25 (Core) 1 x ICPS RL10B (ICPS) |
PBAN Solid LH2 / LOX LH2 / LOX |
269 vac 452,3 vac (4.436 km/s) 465 vac |
| New Glenn (2024) | 1 2 |
7 x BE-3U 2 x BE-3U |
CH4 / LOX CH4 / LOX |
? ? |
| Falcon 9 FT (2018) | 1 2 |
9 x Merlin 1D+ 1 x Merlin ID Vac |
RP-1 / LOX RP-1 / LOX |
311 vac 348 vac |
| Falcon 9 Heavy (2018) | 0 1 2 |
2 x Boosters (2 x 9 Merlin 1D per Booster) 9 x Merlin 1D 1 x Merlin 1D Vac |
Chilled RP-1 / Subcooled LOX Chilled RP-1 / Subcooled LOX RP-1 / LOX |
311 vac 282 vac 348 vac |
| Vulcan Centaur (2024) | 0 1 2 |
0, 2, 4 or 6 GEM-63XL (Booster) 2 x BE-4 (Blue Origin) 2 x RL-10 |
Graphite-Epoxy-Motor (GEM) CH4 / LOX LH2 / LOX |
280 vac ? 454 vac |
| Terran R (2026) | 1 2 |
13 x Aeon R 1 x Aeon Vac |
LCH4 / LOX LCH4 / LOX |
? ? |
| Zhuque-2 (2023) | 1 2 |
4 x TQ-12 1 x TQ-12 + vernier engine |
LCH4 / LOX – |
? |
| – | – – |
– | – – |
– |
Blue Origin BE (Blue Engine) 09-10-2023
- BE-3 (BE-3U and BE-3PM). Family of rocket engines made by Blue Origin with two variants, the BE-3U and BE-3PM. The rocket engine is a liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen (LH2/LOX) cryogenic engine that can produce 490 kN (110,000 lbf) and 710 kN (160,000 lbf) of thrust, respectively.
- BE-4 Liquid oxygen/liquified natural gas (LOX/LNG) rocket engine that can produce 2,400 kN (550,000 lbf) of thrust. In late 2014, the company signed an agreement with United Launch Alliance (ULA) to develop the BE-4 engine, for ULA’s upgraded Atlas V and Vulcan Centaur rockets replacing the RD-180 Russian-made rocket engine. The newly developed heavy-lift launch vehicle will use two of the 2,400 kN (550,000 lbf) BE-4 engines on each first stage. The engine development program for the BE-4 began in 2011. It will power the NG.
- BE-7 Currently under development, is being designed for use on a lunar lander.
- Pusher escape motor. The company partnered with Aerojet Rocketdyne to develop a pusher launch escape system for the New Shepard suborbital crew capsule. Aerojet Rocketdyne provides the Crew Capsule Escape Solid Rocket Motor (CCE SRM) while the thrust vector control system that steers the capsule during an abort is designed and manufactured by Blue Origin.
Hall-effect engine (13-10-2023)
NASA and JPL Hall-effect engine test in deep space with Psyche mission.
In spacecraft propulsion, a Hall-effect thruster (HET) is a type of ion thruster in which the propellant is accelerated by an electric field. Hall-effect thrusters (based on the discovery by Edwin Hall) are sometimes referred to as Hall thrusters or Hall-current thrusters. Hall-effect thrusters use a magnetic field to limit the electrons’ axial motion and then use them to ionize propellant, efficiently accelerate the ions to produce thrust, and neutralize the ions in the plume. The Hall-effect thruster is classed as a moderate specific impulse (1,600 s) space propulsion technology and has benefited from considerable theoretical and experimental research since the 1960s.
Hall thrusters operate on a variety of propellants, the most common being xenon and krypton. Other propellants of interest include argon, bismuth, iodine, magnesium, zinc and adamantane.
Hall thrusters are able to accelerate their exhaust to speeds between 10 and 80 km/s (1,000–8,000 s specific impulse), with most models operating between 15 and 30 km/s. The thrust produced depends on the power level. Devices operating at 1.35 kW produce about 83 mN of thrust. High-power models have demonstrated up to 5.4 N in the laboratory. Power levels up to 100 kW have been demonstrated for xenon Hall thrusters.
As of 2009, Hall-effect thrusters ranged in input power levels from 1.35 to 10 kilowatts and had exhaust velocities of 10–50 kilometers per second, with thrust of 40–600 millinewtons and efficiency in the range of 45–60 percent. The applications of Hall-effect thrusters include control of the orientation and position of orbiting satellites and use as a main propulsion engine for medium-size robotic space vehicles.
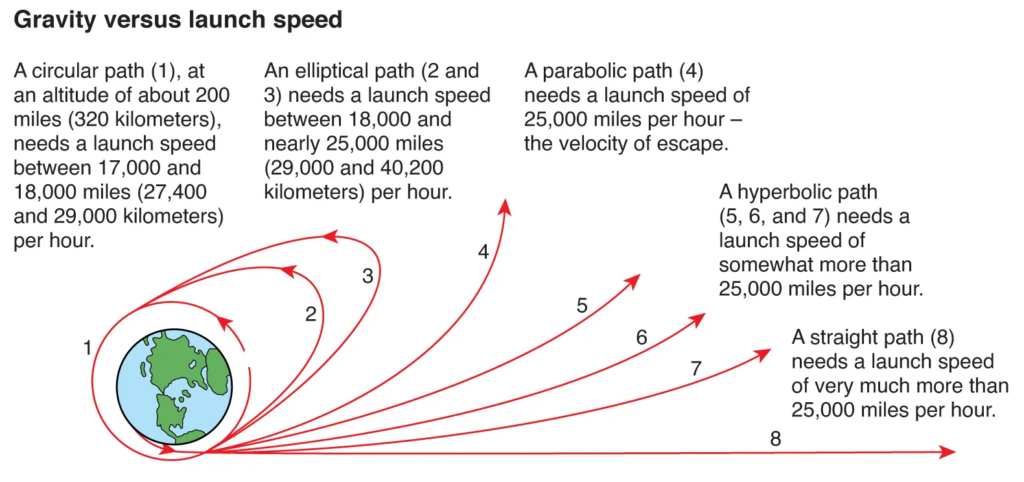
Gravity versus launch speed
Footnote
- Sources: Aerospace dashboard, Artemis I sequence of events, funkystuff.org, Spaceflight Now, Space.com, SpaceNews, Spaceflight.com, SciTechDaily, Launch pad
- Outgoing: NASA, SpaceX, ESA
- Keywords: Performance parameter